

Vitamin D deficiency and coronary artery calcification in subjects with type 1 diabetes.

Young KA, Snell-Bergeon JK, Naik RG, Hokanson JE, Tarullo D, Gottlieb PA, et al.
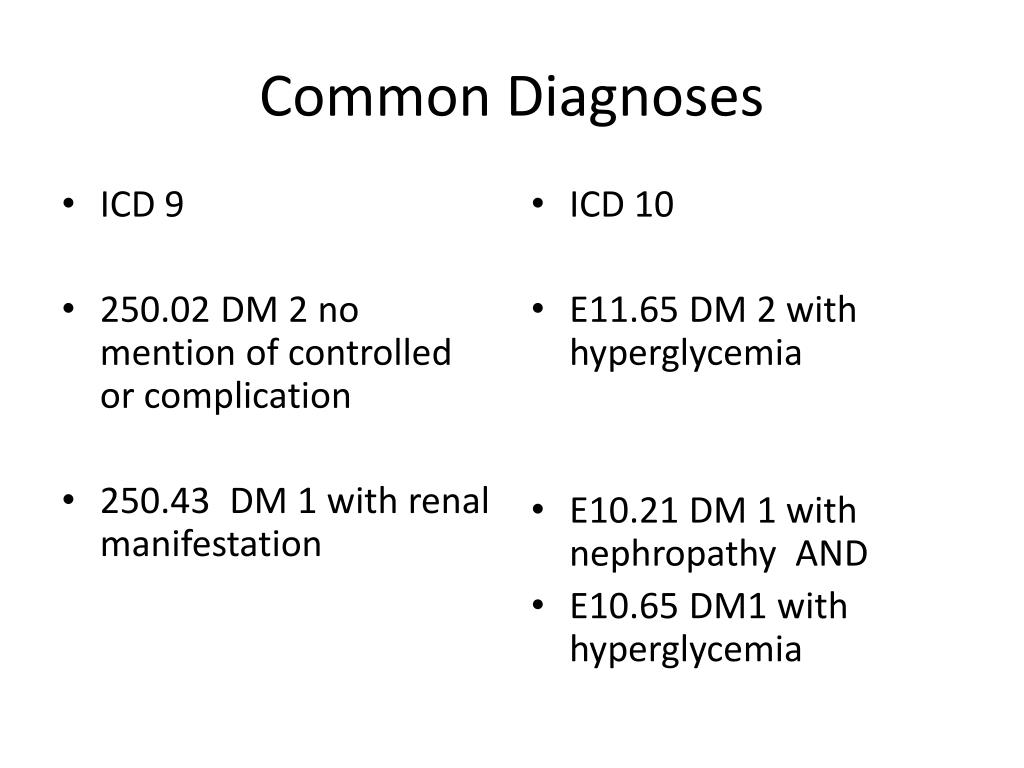
High prevalence of capillary abnormalities in patients with diabetes and association with retinopathy. Genetics of the HLA region in the prediction of type 1 diabetes. Pancreatic volume and endocrine and exocrine functions in patients with diabetes. Philippe MF, Benabadji S, Barbot-Trystram L, et al. Prevalence of Type 1 diabetes autoantibodies (GAD and IA2) in Sardinian children and adolescents with autoimmune thyroiditis. Estimating the cost of type 1 diabetes in the U.S.: a propensity score matching method. Tao B, Pietropaolo M, Atkinson M, Schatz D, Taylor D. A Comparative Effectiveness Analysis of Three Continuous Glucose Monitors. Accessed: January 24, 2013.ĭamiano ER, El-Khatib FH, Zheng H, Nathan DM, Russell SJ. Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Navigator Beats Rival Devices. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2011. Development of Autoantibodies in the TrialNet Natural History Study. International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Advances in management of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Whether the diabetes is transient or chronic was also unknown.Īathira R, Jain V. The researchers suggested, however, that COVID-19 may induce diabetes by directly attacking pancreatic cells that express ACE2 receptors, that it may give rise to diabetes “through stress hyperglycemia resulting from the cytokine storm and alterations in glucose metabolism caused by infection,” or that COVID-19 may cause diabetes via the conversion of prediabetes to diabetes. The study could not specify the type or types of diabetes specifically related to COVID-19, with the report saying that the disease could be causing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes but through differing mechanisms. The investigators, using two US health claims databases, reported that pediatric patients with COVID-19 in the HealthVerity database were 31% percent more likely than other youth to receive a new diabetes diagnosis, while those in the IQVIA database were 166% more likely.
#Icd 10 dm1 with hypoglycemia skin#
foot limited to skin layer due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of left foot with bone necrosis due to diabetes mellitus type 1 Diabetic ulcer of left foot with bone necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer.A study from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicates that SARS-CoV-2 infection increases the likelihood of diabetes developing in children under age 18 years, more than 30 days post infection. with fat layer exposure due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of left foot with muscle necrosis due to diabetes. Diabetic ulcer of foot limited to skin layer due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of foot with bone necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of foot with fat layer exposure due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of foot with muscle necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of heel due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of heel limited to skin layer due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of heel with bone necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of heel with fat layer exposure due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of heel with muscle necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of left foot due to diabetes mellitus type 1 Diabetic ulcer of left foot due to dm 1. with fat layer exposure due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of toe with muscle necrosis due to dm 1 Skin ulcer layer due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of left ankle with bone necrosis due to diabetes mellitus type 1 Diabetic ulcer of left ankle with bone necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of left ankle with fat layer. to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of left ankle with muscle necrosis due to diabetes mellitus type 1 Diabetic. To skin layer due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of ankle with bone necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of ankle with fat layer exposure due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of ankle with muscle necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of calf due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of calf limited to skin layer due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of calf with bone necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of calf with fat layer exposure due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of calf with muscle necrosis due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of left ankle due to diabetes mellitus type 1 Diabetic ulcer of left ankle due to dm 1 Diabetic ulcer of left ankle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
